- The Pound Sterling plummets against its major peers after the release of the weak UK labor market data for the three months ending April.
- UK ILO Unemployment Rate accelerated to 4.6%, the highest level seen since July 2021.
- Investors seek Sino-US trade meeting minutes for fresh cues on the US Dollar’s outlook.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) faces a sharp selling pressure against its peers on Tuesday after the United Kingdom (UK) Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported that the labor market cooled down in three months ending April.
The data showed that the economy added 89K fresh workers, fewer than 112K seen in the quarter ending March. The ILO Unemployment Rate accelerated to 4.6%, as expected, from the prior release of 4.5%. This is the highest level in the jobless rate seen since July 2021. Slowing UK job growth reflects the impact of the increase in employers’ contributions to social security schemes.
UK Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves raised employers’ contribution to National Insurance (NI) from 13.8% to 15% in the Autumn Statement, which became effective in April.
After releasing the labor market data, the ONS stated that “some firms may not be recruiting new workers or replacing leavers.”
Meanwhile, Average Earnings, a key measure of wage growth that drives inflation in the services sector, has grown at a modest pace. Average Earnings Excluding Bonuses rose by 5.2%, slower than estimates of 5.4% and the prior reading of 5.5%, revised lower from 5.6%. The wage growth measure including bonuses grew at a slower pace of 5.3%, compared to expectations of 5.5% and the previous release of 5.6%, revised higher from 5.5%.
Slower wage growth and a slowdown in the labor demand are expected to encourage Bank of England (BoE) officials to reassess their guidance that the central bank will follow a “gradual and cautious” monetary expansion approach, which they delivered in May after lowering interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 4.25%.
Meanwhile, traders are confident that the BoE will keep interest rates steady at 4.25% in the policy meeting on June 19. However, market experts are anticipating that soft labor market data has increased the odds of interest rate cuts in policy meetings later this year. According to analysts at Dutch Bank ING, weak employment data “helps cement cuts in August and November”.
This week, investors should brace for more volatility in the British currency as the monthly Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and factory data for April are scheduled for release on Thursday.
British Pound PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of British Pound (GBP) against listed major currencies today. British Pound was the weakest against the Swiss Franc.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.17% | 0.47% | 0.04% | 0.08% | 0.11% | 0.12% | -0.06% | |
| EUR | -0.17% | 0.31% | -0.15% | -0.06% | -0.04% | -0.05% | -0.21% | |
| GBP | -0.47% | -0.31% | -0.51% | -0.37% | -0.34% | -0.36% | -0.51% | |
| JPY | -0.04% | 0.15% | 0.51% | 0.06% | 0.03% | -0.00% | -0.18% | |
| CAD | -0.08% | 0.06% | 0.37% | -0.06% | 0.02% | 0.02% | -0.14% | |
| AUD | -0.11% | 0.04% | 0.34% | -0.03% | -0.02% | 0.01% | -0.16% | |
| NZD | -0.12% | 0.05% | 0.36% | 0.00% | -0.02% | -0.01% | -0.15% | |
| CHF | 0.06% | 0.21% | 0.51% | 0.18% | 0.14% | 0.16% | 0.15% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the British Pound from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent GBP (base)/USD (quote).
Pound Sterling trades lower against US Dollar amid US-China trade talks
- The Pound Sterling slumps to near 1.3456 against the US Dollar (USD) during European trading hours on Tuesday. The US Dollar trades calmly against its major peers, with investors awaiting the outcome of trade discussions between the United States (US) and China, which started on Monday. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, ticks up to near 99.00.
- The US Dollar had a strong run-up before the Sino-US trade talks in Geneva a few weeks ago. Investors seem to be hesitant to buy on optimism this time as they want concrete trade terms. “A deal to keep talking might be better than nothing, but unless we see a concrete breakthrough, the impact on sentiment is likely to remain muted,” analysts at Saxo Markets said Reuters reported.
- Meanwhile, the White House has expressed confidence that a breakthrough outcome will be achieved after the US-China trade meeting. US National Economic Adviser Kevin Hassett stated in an interview with CNBC on Monday that “export controls to be eased and rare earths to be released in volume” after the meeting.
- During European trading hours, US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick told reporters that trade talks with Beijing are going well and negotiations will likely continue all the day, Reuters reported.
- On the economic calendar front, investors await the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for May, which will be released on Wednesday. The CPI report is expected to show that the headline inflation rose at a faster pace of 2.5% on year, compared to a 2.3% growth seen in April. In the same period, the core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, is anticipated to accelerate to 2.9% from the prior reading of 2.8%. These inflation figures are likely to influence market expectations for the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook.
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, the US central bank is unlikely to cut interest rates before the September monetary policy meeting.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling strives to hold 20-day EMA
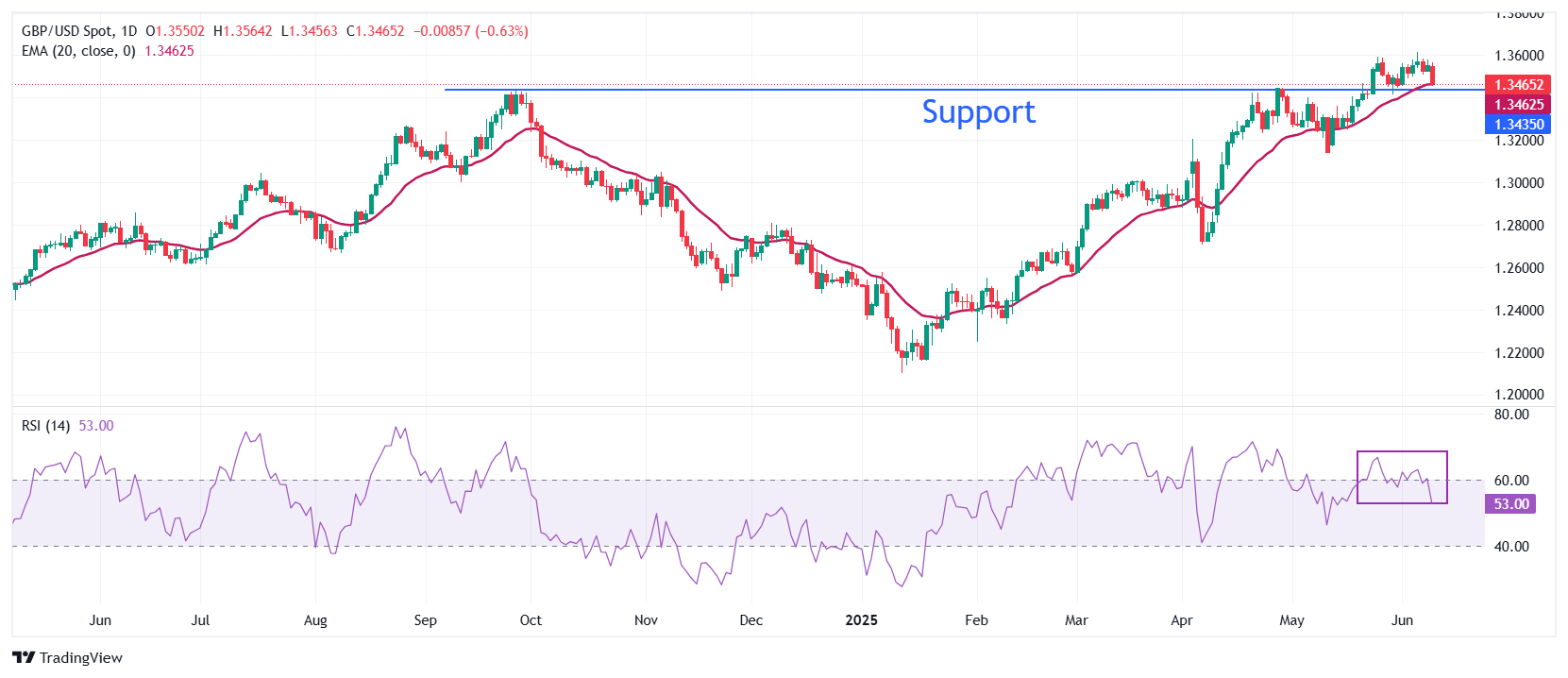
The Pound Sterling slips to near 1.3456 against the US Dollar on Tuesday after failing to revisit the three-year high of 1.3617. The outlook for the pair has become uncertain as it has declined to near the 20-Day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which oscillates around 1.3467.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) faces pressure near 60.00, indicating that the upside is capped.
On the upside, the 13 January 2022 high of 1.3750 will be a key hurdle for the pair. Looking down, the horizontal line plotted from the 26 September 2024 high of 1.3434 will act as a key support zone.
Employment FAQs
Labor market conditions are a key element to assess the health of an economy and thus a key driver for currency valuation. High employment, or low unemployment, has positive implications for consumer spending and thus economic growth, boosting the value of the local currency. Moreover, a very tight labor market – a situation in which there is a shortage of workers to fill open positions – can also have implications on inflation levels and thus monetary policy as low labor supply and high demand leads to higher wages.
The pace at which salaries are growing in an economy is key for policymakers. High wage growth means that households have more money to spend, usually leading to price increases in consumer goods. In contrast to more volatile sources of inflation such as energy prices, wage growth is seen as a key component of underlying and persisting inflation as salary increases are unlikely to be undone. Central banks around the world pay close attention to wage growth data when deciding on monetary policy.
The weight that each central bank assigns to labor market conditions depends on its objectives. Some central banks explicitly have mandates related to the labor market beyond controlling inflation levels. The US Federal Reserve (Fed), for example, has the dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices. Meanwhile, the European Central Bank’s (ECB) sole mandate is to keep inflation under control. Still, and despite whatever mandates they have, labor market conditions are an important factor for policymakers given its significance as a gauge of the health of the economy and their direct relationship to inflation.

